VINYL SIDING: For a piece of Vinyl Siding of nominal skin thickness of
.044” or .046” (these are in fractions in thousandths
of an inch), there are no known published ‘R’
values, as they would be miniscule, if measurable at all.
It is safe to say this value would be nil.
FIBER CEMENT: Builder's News Magazine
states the following: "Fiber cement siding stands up
to the competition: An R-value of about 0.15 for 5/16-inch
thick siding" ....ref:
Builder's News Mag
So,
it is fair to say that neither Fiber Cement Siding, nor Vinyl
Siding have much to offer in the energy savings arena.
It
is in the application of insulation that siding can marry
itself to a formidable ‘R’ rating. Rigid insulation
gives the siding industry its ability to make increased energy
efficiency claims. Iinsulation can be applied to both Fiber
Cement and Vinyl Siding installations and with fantastic results.
Heat resistance: Here is a real world comparison of Vinyl Siding and James Hardie Fiber Cement Siding. It does not
take a rocket scientist to figure that vinyl siding which
is highly combustible would have little or no heat resistance
rating, especially at a little more than the thickness of
a matchbook. In contrast, Fiber Cement Siding is 5/16”
nominal thickness, or ten times the thickness of a nominal
piece of vinyl siding, composed of cement and fibers and
very resistant to heat.
|
|
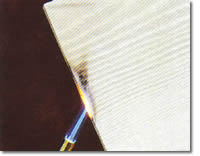
Fiber Cement is Non-Combustible |
Adhered or bonded Vinyl
Siding and Insulation retrofit products have hit the market
with some acceptance. Certain facts should be exposed about
these systems, however. The bonded Vinyl Siding will expand
and contract at a far different rate than the rigid insulation
to which it is attached. Some manufacturers have answered
this dilemma with new insulation products that are less
rigid and more apt to follow the fluctuations of the vinyl.
Alcoa is one with its "Structure" panel that seems to move with the siding and it is "closed cell," so it won't soak up moisture that gets in behind the siding.
Some
of the manufacturers are still marketing their open cell
foam products. Open cell foam is visible as little white
balls compressed together. "This makes the foam soft
or weak, as if it were made of broken balloons or soft toy
rubber balls. The insulation value of this foam is related
to the insulation value of the calm air inside the matrix
of broken cells," as reported by FOAM-TECH.
These cells break apart and the insulation looses its cohesion
when it has become wet. Given the nature of Vinyl Siding
and the fact that it allows moisture to enter behind the siding, what goes on behind the wall that the
homeowner cannot see on the surface is a system in flux
toward failure. At the very least, the ‘R’ value
is usually compromised early on in the system life. In fact,
Open Cell Insulation, the kind that is commonly bonded to
vinyl siding is known to absorb moisture. Given that Vinyl
Siding is known to allow moisture in and labeled a "Supplemental
Rain Screen," by the experts, is it not ironic
that Open Cell Insulation is used when it is known to absorb
moisture and degrade structurally and loose its 'R' value
once wet? "Open
cell foam should never be used for exterior applications,"
according
to Biobased Insulation
.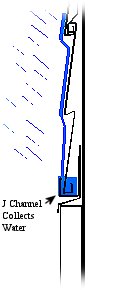 Our page, "'J' Channels and the Problems they Cause" explains the moisture intrusion problem in more detail. Our page, "'J' Channels and the Problems they Cause" explains the moisture intrusion problem in more detail.
 |
Open
Cell Insulation Bonded to Siding |
|
 |
Rigid
Closed Cell Independently & Mechanically
Fastened to Exterior Walls |
|
Vinyl Siding must be installed
loosely and with variances for thermal movement and these
bonded systems leave critical spaces uninsulated at the
channel intersections of ‘J’ channels and Corner
Posts. Cold spots on the interior of the dwelling will be
evident at these junctures during the winter months. The
best way to install an exterior insulation is to install
a rigid closed-cell insulation board, such as Dow Re-siding
Closed Cell Insulation prior to the siding installation.
Fiber Cement, along with solid trim that can
be directly sealed with caulking.
Of most importance, if you are planning on adding insulation, is to consider the Dew Point within the wall.
|











